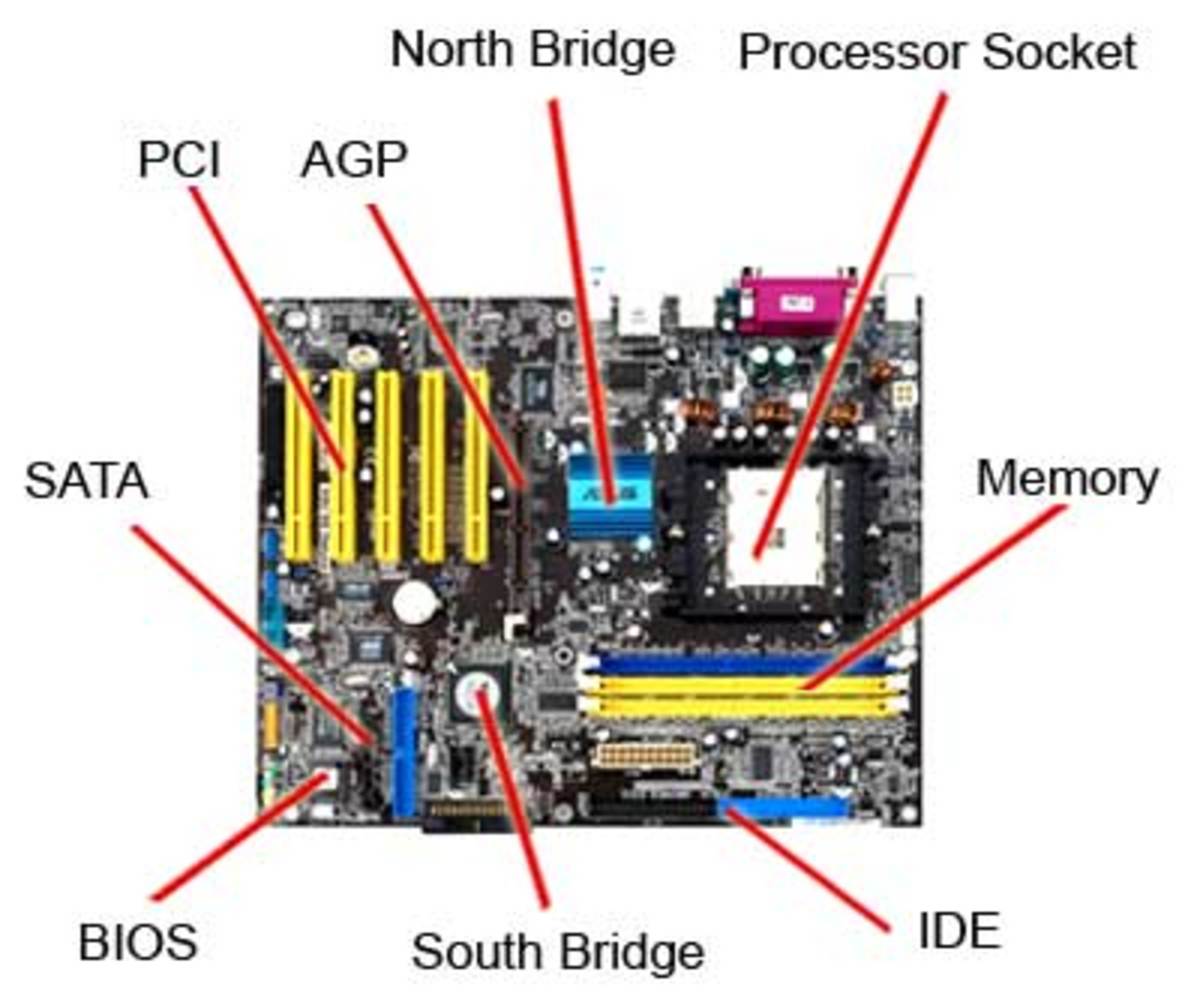
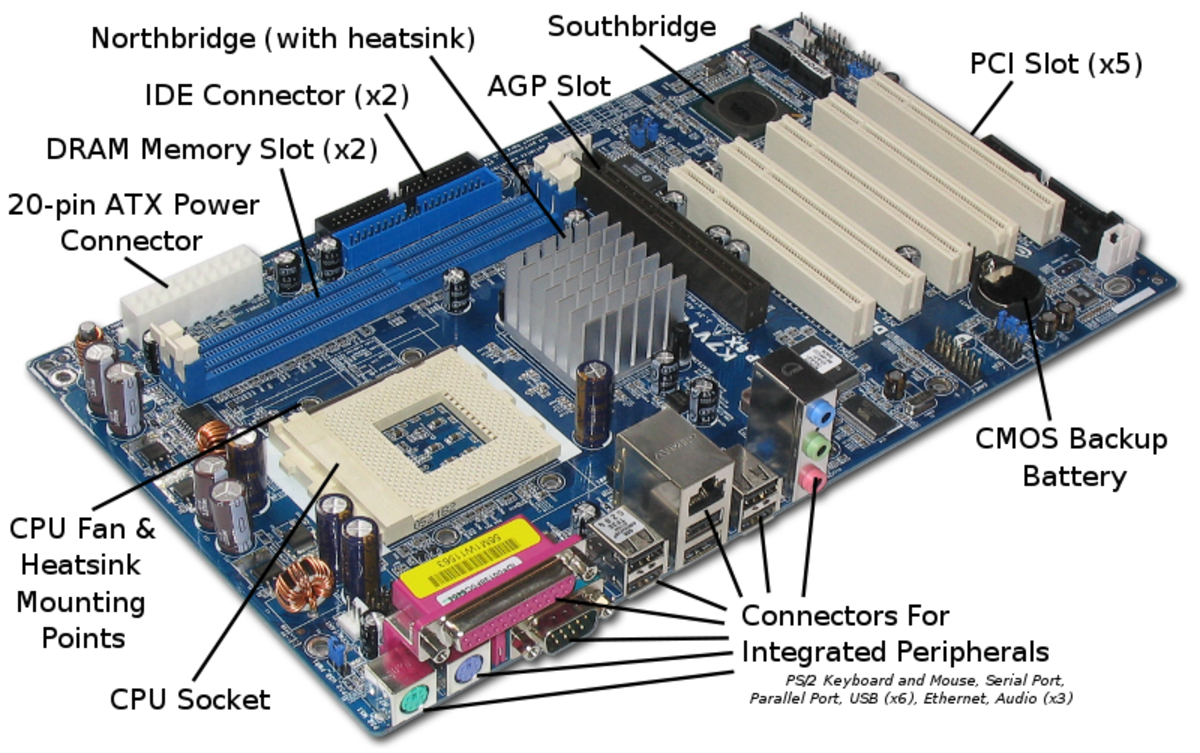
The Parts of a Computer Motherboard and Other Hardware
The CPU Clock
The Switches and Jumpers
- DIP (Dual In-line Package) switches are small electronic switches found on the circuit board that can be turned on or off just like a normal switch. They are very small and so are usually flipped with a pointed object, such as the tip of a screwdriver, a bent paper clip, or a pen top. Take care when cleaning near DIP switches, as some solvents may destroy them. Dip switches are obsolete and you will not find them in modern systems.
- Jumper pins are small protruding pins on the motherboard. A jumper cap or bridge is used to connect or short a pair of jumper pins. When the bridge is connected to any two pins, via a shorting link, it completes the circuit and a certain configuration has been achieved.
- Jumper caps are metal bridges that close an electrical circuit. Typically, a jumper consists of a plastic plug that fits over a pair of protruding pins. Jumpers are sometimes used to configure expansion boards. By placing a jumper plug over a different set of pins, you can change a board's parameters.
- Input devices: For raw data input.
- Processing devices: To process raw data instructions into information.
- Output devices: To disseminate data and information.
- Storage devices: For data and information retention.
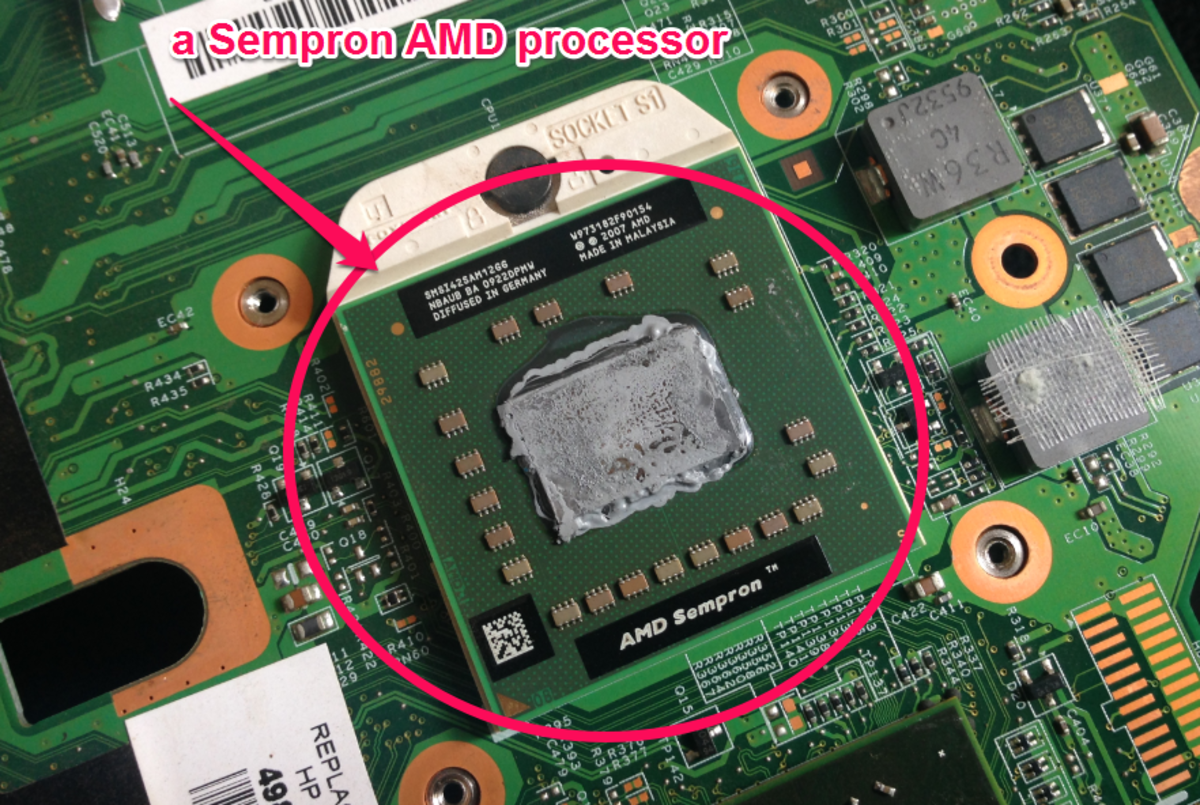
2. Processing Devices
- The control unit: It manages and supervises the operations of the processor and other components that are crucial in data manipulation.
- Arithmetic and logic unit: The ALU is responsible for all arithmetic and logic operations like addition, multiplication, subtraction, division, and comparison logic operations.
- Register and cache: These are storage locations inside the processor that respond to the instructions of the control unit by moving relevant data around during processing.











No comments